Tesla has arguably achieved the feat of being simultaneously the best and most popular at what they do, according to an IDTechEx report.
As the IDTechEx report Electric Vehicles: Land, Sea & Air 2021–2041 discusses, Tesla enters a new market and quickly becomes the top-selling electric vehicle maker: from its home market of California in the US to the major auto markets of Europe, to South Korea and China.
What’s different about a Tesla? The ‘big three’ enabling technologies commonly cited for electric vehicles are the battery, electric traction motor, and power electronics. A statement from IDTechEx says Tesla is on the bleeding edge of all. In this article, IDTechEx explores Tesla’s innovations in the field of power electronics and some of the new materials opportunities being created.
Silicon carbide inverters
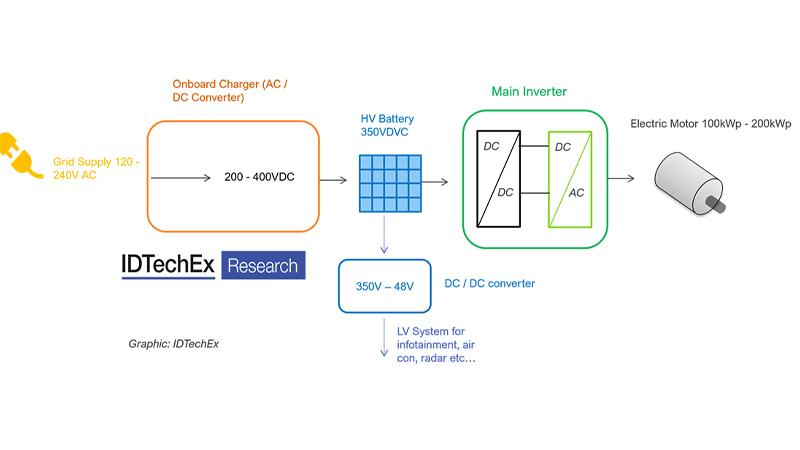
For electric vehicles, power electronics are critical for several functions, but perhaps most critical of all is the main inverter, which converts the DC battery into three-phase AC for the smooth operation of the electric traction motor.
At the core of power electronics devices is power-switch technologies (transistors), which have already seen more than five generations of advancement. Today, silicon insulated-gate bipolar transistors (Si IGBTs) dominate the medium power range, including electric vehicle inverters.
We are now transitioning to a sixth-generation, with wide-bandgap semiconductor materials taking over: silicon carbide (SiC) for high voltage/power applications and gallium nitride (GaN) for lower-voltage and power.
This shift allows smaller and higher-density power modules, operating at higher temperatures, and creates new materials opportunities throughout the power module packaging.
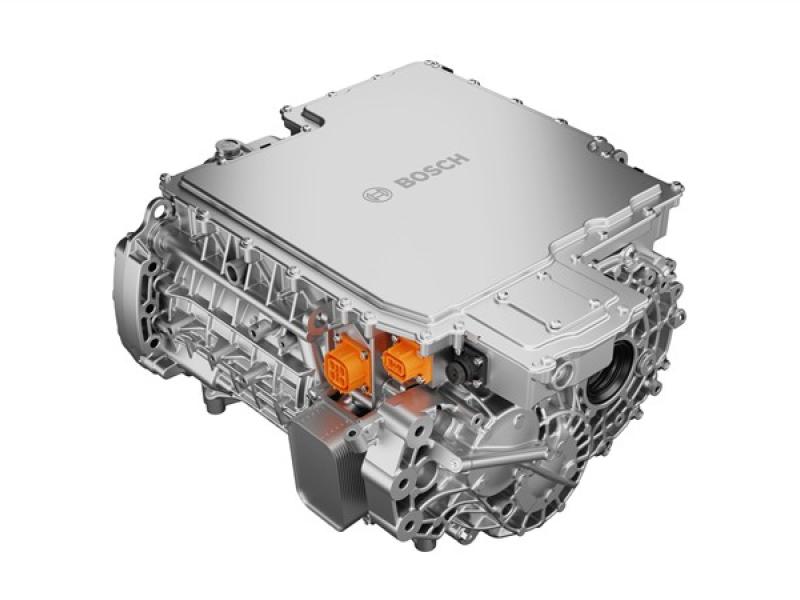
Why is Tesla’s inverter innovative? Well, with the release of the Model 3 in 2018, Tesla became the first company to add SiC metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), sourced from ST Microelectronics, in an in-house inverter design.
The overall design has several innovations beyond the use of SiC packages, but this is the main one. It has led to the overall weight of the inverter (4.8kg) to be under half that of the 2019 Nissan Leaf (11.15kg) and over a third less than that of the Jaguar I-PACE (8.23kg), which use Si IGBT inverters and off-the-shelf parts.
The use of SiC MOSFETs further creates new materials opportunities as the limits of traditional materials are stretched. To deal with the greater areal power densities, a Cu lead frame (metal structures that carry signals from the die to the rest of the inverter) is used over more conventional Al wire bonds.
The die-attach material has also transitioned away from conventional solders towards Ag sintered die-attach materials to handle the higher temperatures.
What’s the catch? As with any emerging technology, the cost has been the main barrier for uptake of SiC MOSFETs and other enabling materials in the power module packages.
But Tesla seems to have solved this too: its inverter has undergone a remarkable cost decline in only three years. The chart shows an experience curve, calculated by IDTechEx, based on cost estimates for the Model 3 inverter in 2018 and a second-gen of the same inverter from the Model Y in 2020. As can be seen, Tesla’s SiC inverter already looks to be on par with Si IGBT modules used in the 2019 versions of the Nissan Leaf and the Jaguar I-PACE.
The result is Tesla’s overall inverter and permanent magnet motor combination is one of (if not the) best on the market, achieving a 97 percent efficiency, yielding more range without increasing expensive battery capacity. All at a similar cost to the older technologies being displaced.
To learn more about innovations in electric cars and the new materials opportunities being created, the IDTechEx reports Advanced Electric Cars 2020-2040 and Materials for Electric Vehicles: Electric Motors, Battery Cells & Packs, HV Cabling 2020-2030 cover trends in the core enabling powertrain technologies, from motors to batteries to autonomous vehicles. See www.IDTechEx.com/cars and www.IDTechEx.com/EVMat.
For more information on the overview report Electric Vehicles: Land, Sea & Air 2021–2041, see www.IDTechEx.com/EV, and also www.IDTechEx.com/Research/EV.