Courtesy Autodata
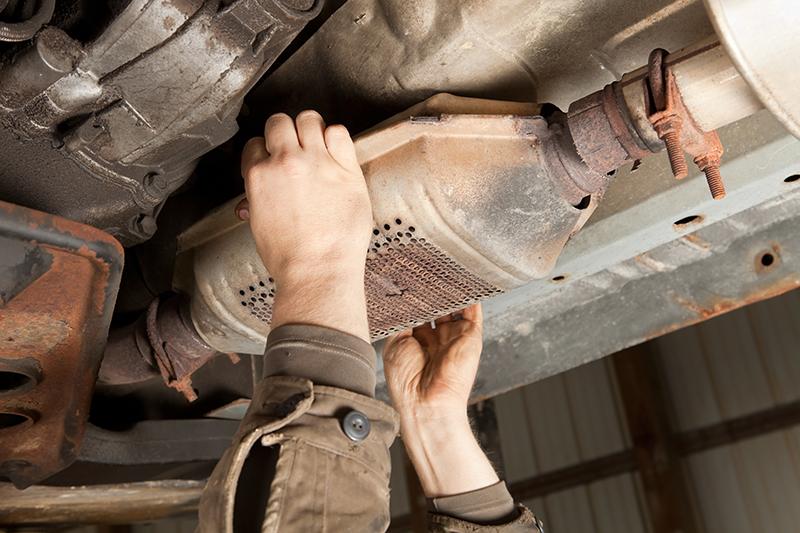
Understanding how catalytic converters work and how to troubleshoot and fix these incredibly useful – and ground breaking – components is a must-have skill automotive technicians need to possess. This month our team provides a deep dive into the operation, lifespan, and most common faults of the catalytic converter.
How do catalytic converters work?
The primary function of a catalytic converter is converting harmful engine emissions like carbon monoxide and various nitric oxides into less toxic gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor via powerful chemical reactions.
Catalytic converters use catalysts – precious metals like platinum, palladium, and rhodium – that operate at a high temperature and accelerate chemical reactions.
These catalysts are coated inside the honeycomb structure of the catalytic converter to increase the surface area. When exhaust gases make contact, they initiate a chemical reaction to break down harmful gasses and convert them into less toxic forms.
The number of catalytic converters used in each vehicle will vary depending on the type of vehicle and the number of exhaust pipes present.
High-end cars, for example, use two catalytic converters in sequence to minimise harmful emissions while vehicles with more than one exhaust pipe use several converters in parallel—one for each exhaust pipe.
That said, most vehicles only use a single catalytic converter in their exhaust system.
How do motor mechanics spot a faulty catalytic converter?
These components generally last up to 10 years – and most vehicle owners may never need to repair or replace their units in their lifetime.
That said, catalytic converters can get damaged or become less effective for several reasons, including inefficient air/fuel mixtures, faulty spark plugs and oxygen sensors, and incorrect engine timing.
In most of these instances, the converter units overheat and melt the internal honeycomb structure, reducing their operational effectiveness.
Catalytic converters may also get fully or partially clogged up due to antifreeze and oil leaks caused by failed gaskets, damaged valve seals, and worn pistons.
Today, there are a few tell-tale signs of faulty catalytic converters you can keep an eye out for, for a more efficient and accurate diagnosis.
A lack of acceleration
The engine depends on the efficient flow of exhaust gases to operate at an optimal level. Blocks in the catalytic converter may restrict the flow of exhaust gasses, hindering engine performance.
High fuel consumption
High fuel consumption is a side effect of poor acceleration—to get more acceleration, the engine injects more fuel into the pistons than usual, leading to poor fuel efficiency.
Rattling noises
Motor mechanics may notice a rattling noise when a given vehicle is idle or being driven due to a broken catalytic converter. The dislodged metal pieces of the honeycomb structure may enter the muffler, causing the vehicle to stall due to the blockage.
The check engine light will turn on
Most modern vehicles contain oxygen sensors that monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. The sensor will trigger the check engine light if the catalytic converter is damaged or operating below the optimum level.
The smell of rotten eggs in the exhaust gas
Gasoline normally contains trace amounts of sulphur, which turn into sulphide, and has a rotten egg smell, during the combustion process. Catalytic converters mask this smell by converting sulphide into odourless sulphur dioxide. Faulty units fail in the conversion process.
What is the best way to fix issues related to catalytic converters?
The best course of action motor mechanics can take to fix issues related to catalytic converters is to replace older units with new ones. That said, if a catalytic converter is not physically damaged, cleaning the unit can restore its efficiency.
Technicians can also advise their clients to use lead-free fuels, which improve the effectiveness of the catalysis process.
Optimising how catalytic converters are used is crucial in our fight against climate change
When it comes to modern vehicles, catalytic converters play a critical role in ensuring vehicles comply with emission standards and minimise the environmental impact the transportation industry has on the planet.
As such, troubleshooting and fixing catalytic converters is a skill motor mechanics can improve on to do their part in ensuring the industry operates as sustainably as possible.