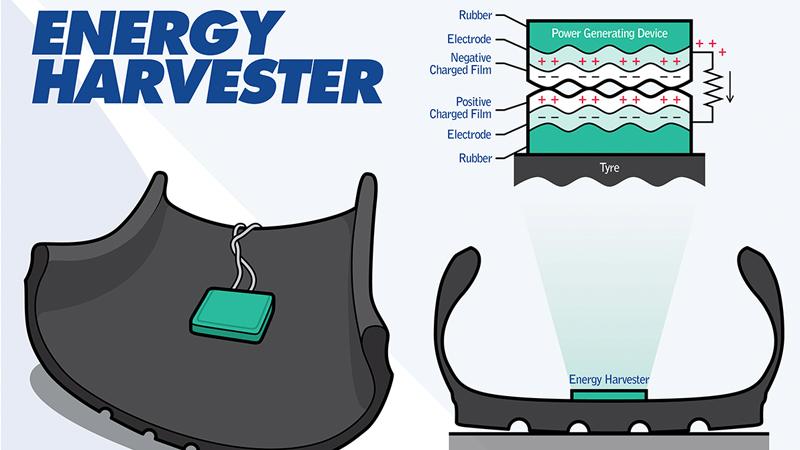
In 2019 Sumitomo Rubber Industries (SRI) and Kansai University in Japan announced a new technology that generates electric power from the rotation of a tyre. By installing an energy harvester inside a tyre, static electricity can be converted to clean energy.
The energy harvester takes advantage of a type of static electricity called frictional charging, which is formed each time a tyre’s footprint deforms as it rotates along the road. It is believed that this technology holds great potential for practical applications such as a power source for automotive digital tools.
Now further research has revealed that it’s possible for the harvester to supply power to peripheral tyre sensors, such as tyre pressure monitoring system (TPMS) sensors, without the need for batteries.
SRI has developed an integrated system which uses the electricity generated by the energy harvester to charge a power control until, which in turn activates and supplies power to an external sensor. During speeds of 50km/h, the system produces more than 800 microwatts of power – enough to activate an external sensor and achieve continuous Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) transmission.